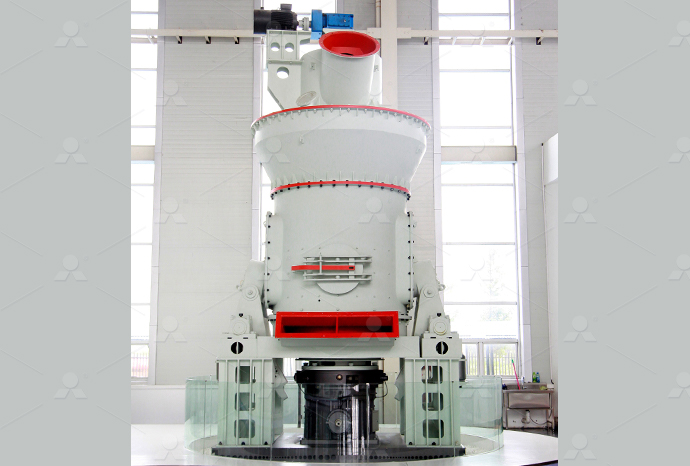
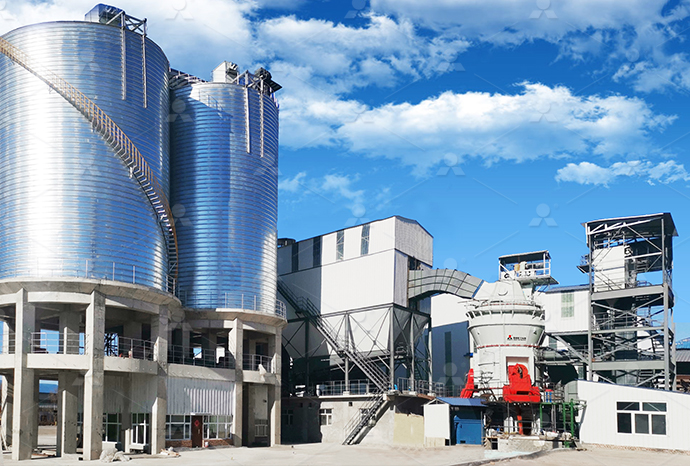
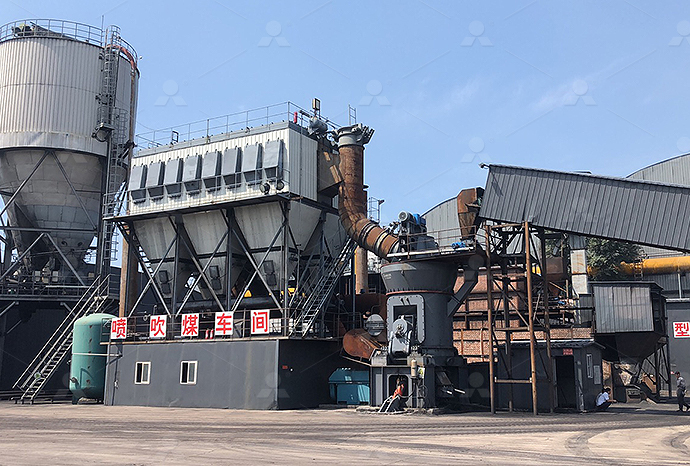
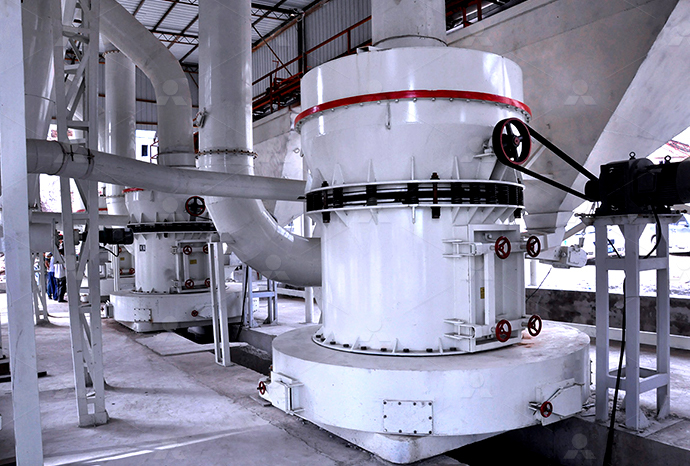
Igneous rock limestone powder production line igneous rock production

Production and Uses of Crushed Rock Aggregates: An Overview
2018年12月11日 Igneous rocks: These rocks are primarily crystalline and are formed by the cooking of molten rock material beneath the earth’s crust (magma) Sedimentary rocks: These rocks are formed from deposited insoluble material (eg the remains of existing rock deposited 2017年9月1日 In this study, we advance our knowledge of heat production throughout the lithosphere by analyzing chemical analyses of 108,103 igneous rocks provided by a number of On the radiogenic heat production of igneous rocks2021年10月3日 The production of crushed rock aggregate involves the process of mining known as quarrying and it also has some environmental impacts such as noise pollution as a result of explosives and heavyProduction and Uses of Crushed Rock Aggregate from 2024年1月31日 Igneous rocks form through the cooling and solidification of magma or lava These rocks are distinctly different from sedimentary and metamorphic rocks, which originate from the deposition of material at the Igneous Rocks – Types, Properties, and Examples
.jpg)
Introduction to Metamorphic Rocks, Rock Metamorphism, and
The local imbalances causing chemical reactions in rocks are produced by large scale geologic processes including igneous intrusions, basin subsidence and plate movements (lithospheric Igneous rocks are one of the three main types of rocks found on Earth, the other two being sedimentary and metamorphic rocks These rocks form from the solidification and cooling of molten material, known as magma, which Igneous Rocks Types, Classification, Properties, Igneous and sedimentary carbonate rocks display no apparent differences in the field and at meso–microscale They may be layered, massive crystalline or show discrete clasts in a matrix, which make both rock types resemble one another Igneous and sedimentary ‘limestones’: the puzzling Igneous rocks form when molten material cools and hardens They may form either below or above Earth’s surface They make up most of the rocks on Earth Most igneous rock is buried below the surface and covered with sedimentary 41: Igneous Rocks Geosciences LibreTexts
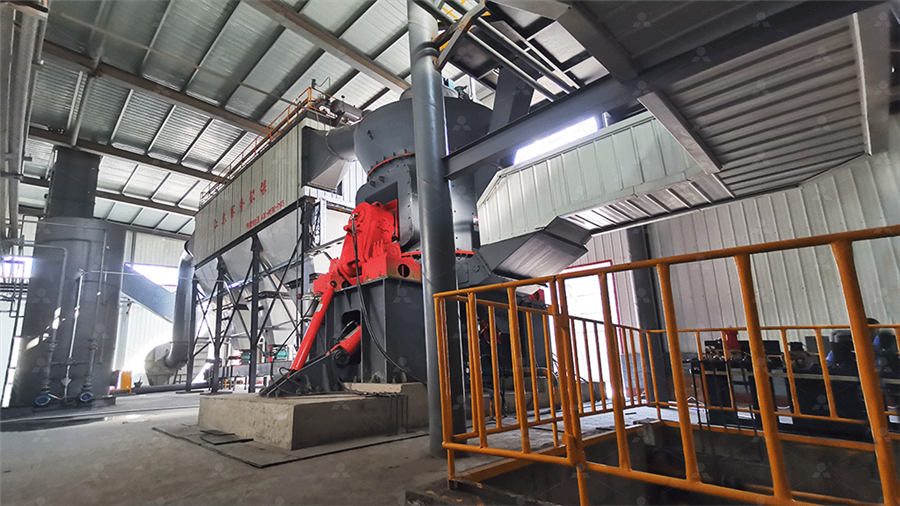

41: Igneous Rocks Geosciences LibreTexts
Pumice is another example of an igneous rock (Figure 42) Pumice is used to make stonewashed denim jeans! Pumice stones are put into giant washing machines with newlymanufactured jeans and tumbled around to give jeans 2024年1月28日 In order to investigate the influence of igneous rock powder and silica fume on the performance of cement mortar, facilitate the application of igneous rock powder in engineering, and promote the Evaluation of Workability and Mechanical Properties in Cement Igneous rocks are one of the three main types of rocks found on Earth, the other two being sedimentary and metamorphic rocks These rocks form from the solidification and cooling of molten material, known as magma, which Igneous Rocks Types, Classification, Properties, 2024年1月28日 In order to investigate the influence of igneous rock powder and silica fume on the performance of cement mortar, facilitate the application of igneous rock powder in engineering, and promote the greening of the cement industry, this study examined the pozzolanic activity of three different types of igneous rock powders: granite, andesite, and tuff It explored Evaluation of Workability and Mechanical Properties in Cement

The Rock Cycle Diagram and Explanation Science Notes and
2023年8月22日 Steps of the Rock Cycle Molten rock called magma is the source material for rocks Igneous rocks form both under the surface and above it when magma becomes lava Heat and pressure changes igneous and sedimentary rocks into metamorphic rocks Erosion and weathering break igneous and sedimentary rocks up, which compact into sedimentary rocksHello everyone!Today, we're building a contraption to gather igneous rock from a volcano and cool it down for usage Hope you enjoy!:)Oxygen Not Included is IGNEOUS ROCK PRODUCTION Spaced Out: Ep #87 (Oxygen The rock cycle simply moves from the igneous to metamorphic to sedimentary rocks and the process repeats itself over and over When these materials eventually harden, they produce sedimentary rocks Examples of sedimentary rocks include mudstone, limestone, sandstone, and conglomerate Sedimentary rocks are largely grouped into three: The Rock Cycle: Igneous, Sedimentary, and Metamorphic Rocks2024年1月31日 1 Felsic Igneous Rocks Definition: Felsic rocks are rich in silica (over 65%) and contain a high proportion of lighter minerals like quartz and feldsparThe term “felsic” derives from “feldspar” and “silica” Characteristics: These rocks are generally light in color, ranging from white to pink or light greyThey have a high content of aluminum, potassium, and sodiumIgneous Rocks Types, Properties, and Examples Science Notes
.jpg)
Igneous Rocks National Geographic Society
2023年10月19日 Igneous rocks form when magma (molten rock) cools and crystallizes, either at volcanoes on the surface of the Earth or while the melted rock is still inside the crust All magma develops underground, in the lower crust or upper mantle, because of the intense heat there Igneous rocks can have many different compositions, depending on the magma they cool from2017年11月1日 We analyze the heat production of ∼ 204,000 whole rock geochemical analyses to quantify how heat production of these rocks varies with respect to chemistry and their evolution during metamorphismOn the radiogenic heat production of metamorphic, igneous, Composition Composition refers to a rock’s chemical and mineral makeup For igneous rocks, composition is divided into four groups: felsic, intermediate, mafic, and ultramafic These groups refer to differing amounts of silica, iron, and 41: Classification of Igneous Rocks Geosciences Types of Igneous Rocks Igneous rocks are divided into two main types based on where they cool and solidify: Intrusive Igneous Rocks Intrusive igneous rocks, also known as plutonic rocks, are formed when magma cools and solidifies Igneous Rocks: Formation, Classification, Examples, Uses
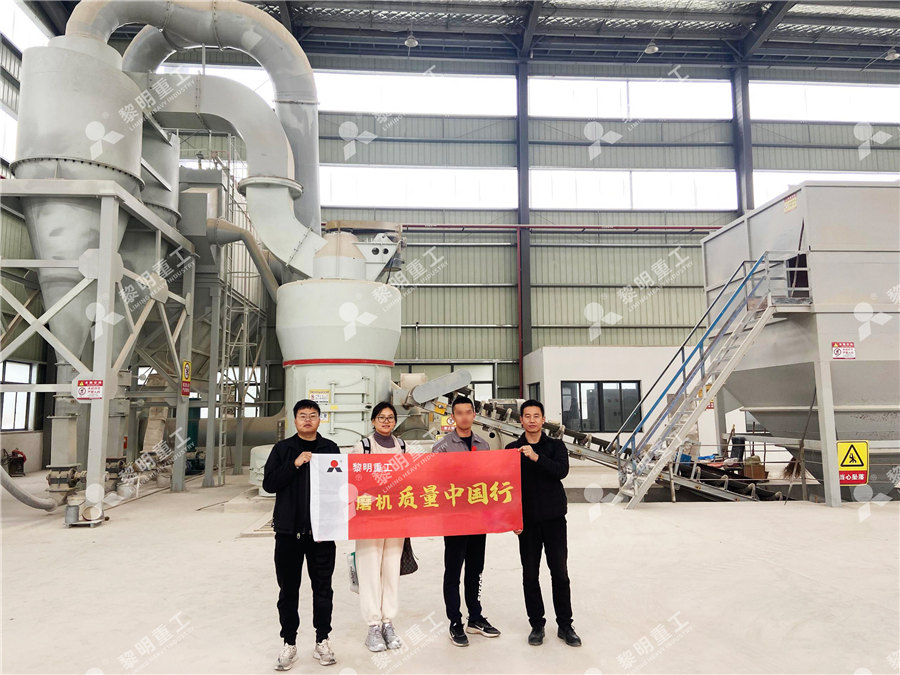

(PDF) Phosphate Rocks: A Review of Sedimentary and
2021年10月16日 phatic limestone, or phosphatic marl, and the nonphosphatic layers correspond mostly to marls, limestones, dolomites, and clays/silts (Figure 6 ) Minerals 2021 , 11 , x FOR PEER REVIEW 9 of 年3月21日 Geothermal resources have become a key clean energy source for research and development owing to their cleanliness and renewability The geothermal resources that are presently exploited and used worldwide are mainly within hydrothermal systems []However, hot dry rock (HDR) resources are gaining increasing attention from governments, research Heat Generation and Accumulation for Hot Dry Rock Resources in Igneous Rock Textures The texture of an igneous rock results from the cooling, crystallization, and solidification history of the magma that formed it Once you know the texture of an igneous rock, you can usually deduce from the texture whether it 36: Igneous Rocks Geosciences LibreTextsLimestone (calcium carbonate CaCO 3) is a type of carbonate sedimentary rock which is the main source of the material limeIt is composed mostly of the minerals calcite and aragonite, which are different crystal forms of CaCO 3Limestone forms when these minerals precipitate out of water containing dissolved calcium This can take place through both biological and nonbiological Limestone Wikipedia
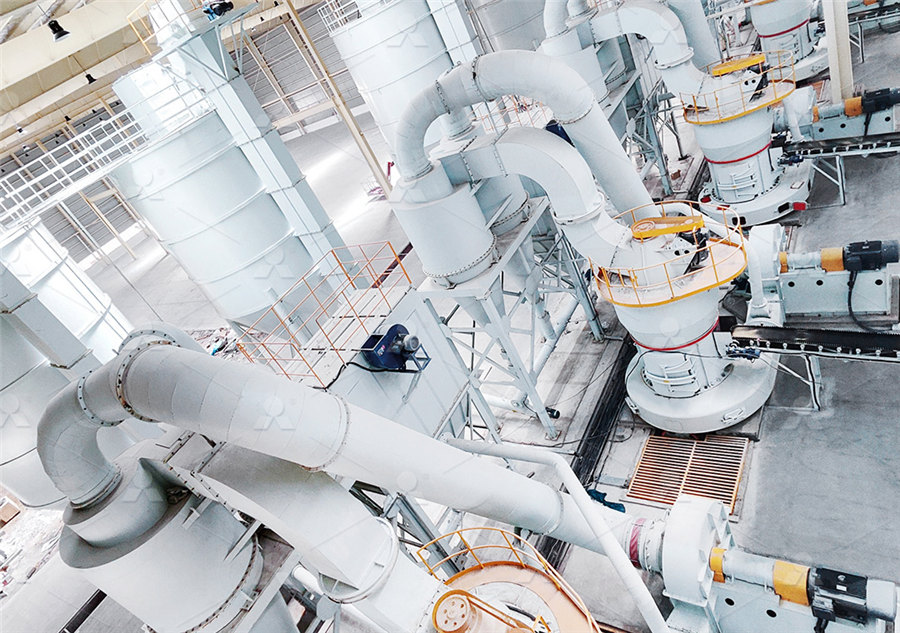

Igneous Rocks: Formation, Types and Examples Earth Eclipse
Igneous rocks form from the cooling of magma – molten materials in the earth’s crust The terminology Igneous means fire or heat In this sense, igneous rocks are formed when molten rock (magma) solidifies either underneath the earth’s crust to form plutonic (intrusive) igneous rocks or on the surface of the earth to form volcanic (extrusive) igneous rocks2020年9月19日 Igneous rocks are essentially crystallisation products of natural, hot melts, derived from the Earth’s interior, known as magmaThe overwhelming majority of magmas are of silicate composition, whereas carbonate, oxide or sulfide magmas are much rarer Commonly, magmas do not consist only of a homogeneous liquid but contain in addition variable amounts Igneous Rocks SpringerLinkMarble Chalk The Giant’s Causeway All made of rock but all different Learn all about the three different types of rock found on Earth with BBC BitesizeRock types The Earth and atmosphere KS3 Chemistry BBCFigure 413 is a diagram with the minerals from Bowen’s reaction series, and is used to decide which name to give an igneous rock Figure 413 Classification diagram for igneous rocks Igneous rocks are classified according to the relative abundances of minerals they contain A given rock is represented by a vertical line in the diagram43 Classification of Igneous Rocks – Principles of Earth Science

6 Igneous Rocks and Silicate Minerals – Mineralogy
Sometimes extrusive igneous rocks cool so quickly that no crystals form This is especially likely to happen if lava meets water The result is a rock composed of volcanic glass called obsidianExamples of obsidian appeared in Figures 121 Phosphate rock is mostly produced in sedimentary rocks, but also in metamorphic rocks and igneous rocks Except for some cases, phosphorus in minerals always exists in the form of orthophosphate, and the main mineral of phosphorus is apatite Phosphorus is an important chemical raw material and an essential element forPhosphate Rock Production LineGabbro is a coarsegrained mafic igneous rock, made with mainly mafic minerals like pyroxene and only minor plagioclase Because mafic lava is more mobile, it is less common than basalt Gabbro is a major component of the lower oceanic 41: Classification of Igneous Rocks Geosciences Sedimentary rock and the processes that create it, which include weathering, erosion, and lithification, are an integral part of understanding Earth ScienceThis is because the majority of the Earth’s surface is made up of sedimentary rocks and their common predecessor, sedimentsEven though sedimentary rocks can form in drastically different ways, their origin and creation have 5 Weathering, Erosion, and Sedimentary Rocks Virginia Tech
G[R.jpg)
Igneous Rocks Geology (US National Park Service)
Igneous rocks are classified both by their chemical composition, mineral composition, texture, and structure Texture and structure refer to the relationships between crystals, groundmass, vesicles, and other components of a rock Composition and Minerals Igneous rocks are mostly made of the most common elements found in the Earth’s crustExtrusive igneous rock; Intrusive igneous rock; Answer: b) Intrusive igneous rock Explanation: Granite is formed below the earth’s surface resulting in large crystals when cooling takes place Hence it is classified as intrusive igneous rock 5 Cooling and solidification of magma or lava lead to the formation of rock Metamorphic Igneous Rocks Questions Practice Questions with AnswersLimestone is a very common sedimentary rock consisting of calcium carbonate (more than 50%) It is the most common nonsiliciclastic (sandstone and shale are common siliciclastic rocks) sedimentary rockLimestones are rocks that are composed of mostly calcium carbonate (minerals calcite or aragonite) Carbonate rocks where the dominant carbonate is dolomite (calcium Limestone Sedimentary rocks Sandatlas413 Igneous Rock Bodies Igneous rocks are common in the geologic record, but surprisingly, it is the intrusive rocks that are more common Extrusive rocks, because of their small crystals and glass, are less durable Plus, they are, by definition, exposed to the elements of erosion immediately Intrusive rocks, forming underground with larger, stronger crystals, are more 4 Igneous Processes and Volcanoes – An Introduction to Geology
.jpg)
The Rock Cycle Education
2023年12月13日 There are three main types of rocks: sedimentary, igneous, and metamorphic Each of these rocks are formed by physical changes—such as melting, cooling, eroding, compacting, or deforming —that are part of the rock cycle Sedimentary Rocks Sedimentary rocks are formed from pieces of other existing rock or organic material There are three different 2024年11月12日 Igneous rock, any of various crystalline or glassy rocks formed by the cooling and solidification of magma, which is a hot (600 to 1,300 °C, or 1,100 to 2,400 °F) molten or partially molten rock Igneous rocks constitute one of the three principal classes of rocks, the others being metamorphic and sedimentaryIgneous rock Characteristics, Examples, Formation, TypesPumice is another example of an igneous rock (Figure 42) Pumice is used to make stonewashed denim jeans! Pumice stones are put into giant washing machines with newlymanufactured jeans and tumbled around to give jeans 41: Igneous Rocks Geosciences LibreTexts2024年1月28日 In order to investigate the influence of igneous rock powder and silica fume on the performance of cement mortar, facilitate the application of igneous rock powder in engineering, and promote the Evaluation of Workability and Mechanical Properties in Cement
.jpg)
Igneous Rocks Types, Classification, Properties,
Igneous rocks are one of the three main types of rocks found on Earth, the other two being sedimentary and metamorphic rocks These rocks form from the solidification and cooling of molten material, known as magma, which 2024年1月28日 In order to investigate the influence of igneous rock powder and silica fume on the performance of cement mortar, facilitate the application of igneous rock powder in engineering, and promote the greening of the cement industry, this study examined the pozzolanic activity of three different types of igneous rock powders: granite, andesite, and tuff It explored Evaluation of Workability and Mechanical Properties in Cement 2023年8月22日 Steps of the Rock Cycle Molten rock called magma is the source material for rocks Igneous rocks form both under the surface and above it when magma becomes lava Heat and pressure changes igneous and sedimentary rocks into metamorphic rocks Erosion and weathering break igneous and sedimentary rocks up, which compact into sedimentary rocksThe Rock Cycle Diagram and Explanation Science Notes and Hello everyone!Today, we're building a contraption to gather igneous rock from a volcano and cool it down for usage Hope you enjoy!:)Oxygen Not Included is IGNEOUS ROCK PRODUCTION Spaced Out: Ep #87 (Oxygen

The Rock Cycle: Igneous, Sedimentary, and Metamorphic Rocks
The rock cycle simply moves from the igneous to metamorphic to sedimentary rocks and the process repeats itself over and over When these materials eventually harden, they produce sedimentary rocks Examples of sedimentary rocks include mudstone, limestone, sandstone, and conglomerate Sedimentary rocks are largely grouped into three: 2024年1月31日 1 Felsic Igneous Rocks Definition: Felsic rocks are rich in silica (over 65%) and contain a high proportion of lighter minerals like quartz and feldsparThe term “felsic” derives from “feldspar” and “silica” Characteristics: These rocks are generally light in color, ranging from white to pink or light greyThey have a high content of aluminum, potassium, and sodiumIgneous Rocks Types, Properties, and Examples Science Notes 2023年10月19日 Igneous rocks form when magma (molten rock) cools and crystallizes, either at volcanoes on the surface of the Earth or while the melted rock is still inside the crust All magma develops underground, in the lower crust or upper mantle, because of the intense heat there Igneous rocks can have many different compositions, depending on the magma they cool fromIgneous Rocks National Geographic Society2017年11月1日 We analyze the heat production of ∼ 204,000 whole rock geochemical analyses to quantify how heat production of these rocks varies with respect to chemistry and their evolution during metamorphismOn the radiogenic heat production of metamorphic, igneous,